
Table of Contents
ToggleWhen new riders consider entering the motorcycle market, one of the most important questions that pops up: what is the highest cc without a motorcycle license? The answer also matters to those who are planning to ride and those companies in the process of customizing product lines to different regions.
In the majority of jurisdictions in the world, a 50cc motorcycle may be ridden without a motorcycle license class endorsement. But details vary greatly depending on the state, country, and licensing system.
This article explores the legal implications, safety standards, and business aspects of motorcycle licensing and cc limits worldwide.
A motorcycle license class is more of a driving license endorsement or category of driving license. It permits one to have their motorcycle on the road lawfully. Countries and states group licenses in levels and classes depending on the engine size, speed capacity, and the experience of the rider. These classes ensure that new riders start with smaller, less powerful bikes before progressing to high-performance motorcycles.
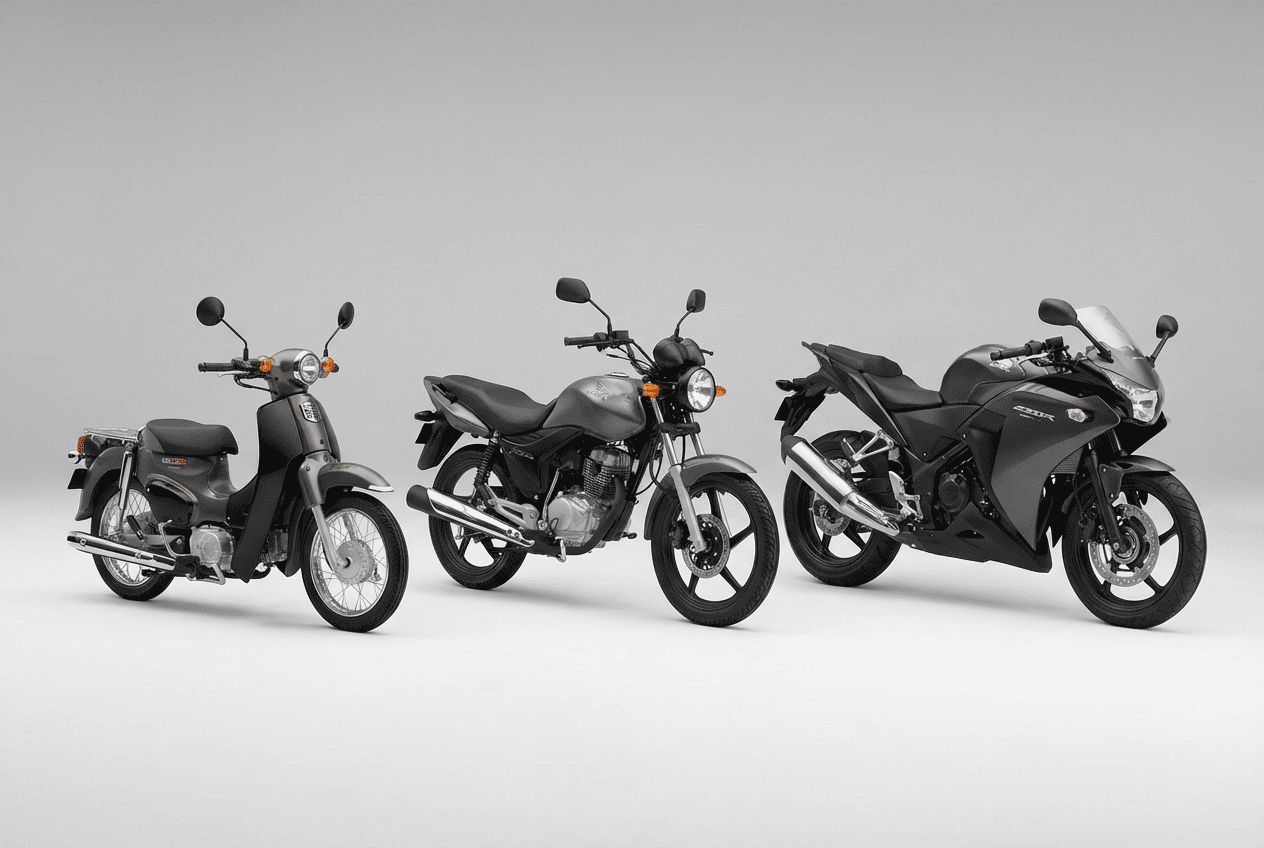
Motorcycles are commonly classified by cubic centimeters (cc):
Globally, systems differ. or.S., licensing depends on individual state laws, while Europe uses a structured licence moto system with categories such as AM (50cc mopeds), A1 (125cc), A2 (restricted 35kW), and A (unrestricted).
For businesses, this variation means adapting product portfolios to meet regional licensing requirements.

The answer is yes, you require a license to ride a motorcycle, but there are minor exceptions to this rule (mopeds or scooters that come under 50cc should be allowed). The majority of jurisdictions set 16 as the age limit for riders of mopeds and 18 of larger bikes. Riders are also generally issued a motorcycle permit and then upgraded to a full endorsement.
Riding without a license possibly results in significant penalties. These are the penalties the riders should be mindful of:
Apart from the penalties, there are several safety and insurance implications involved. Operating outside licensing laws raises liability risks. Insurance providers enforce motorcycle license class rules strictly, and claims may be denied if the rider is unlicensed.
The general rule is simple: 50cc and under is the usual limit. However, Mopeds and scooters coming under this range are exempt from motorcycle licensing. Yet the details shift when comparing different regions. Here’s a complete comparison of street legality restriction levels based on the CC of a bike according to the regions:
In the U.S., states like Oregon define a moped as having a combustion engine of 35.01–50 cc, a maximum speed of 30 mph, and require a standard driver’s license (Class C) but not a motorcycle endorsement, per ORS 801.345 and ORS 807.010.
Source: OregonLaws and Team Oregon.
In California, mopeds (“motor-driven cycles”) under 150 cc require a motorcycle license (M1 or M2) as per CVC 405, while mopeds defined under CVC 406 still fall under that licensing requirement. Businesses should note such nuances when distributing across states.
Source: DMV California and svhlaw.com
Under the EU framework for Europse, mopeds (category AM) are officially defined as two-wheeled, mechanically propelled vehicles, limited to a design speed of no more than 45 km/h. Riders can qualify as early as 16, with fewer licensing demands than higher categories.
Source: RSA and Mobility & Transport – Road Safety.
Australia employs the Learner Approved Motorcycle Scheme (LAMS) for novice riders. Under this scheme, motorcycles with engine capacity up to 660 cc, power-to-weight ratio not exceeding 150 kW/tonne, and up to 25 kW for electric bikes are approved as learner-friendly. However, the general exemption of a 50 cc limit without license does not apply. Novice riders must still hold the appropriate RE-class licence and ride only LAMS-approved models
Source: NSW Government and NSW Gov
For Asian regions such as Southeast Asia, there is no general legal allowance for riding ≤ 50 cc without a license. That misconception persists among travelers, but local laws uniformly require motorcycle licensing. That’s simply because rental shops might tolerate it does not make it lawful.
Source: worldnomads.com and Travel Stack Exchange.
The motorcycle licence CC limit varies with the geographical region. We’ve explained the CC limit for all major regions in detail:
In most states, how many cc require a motorcycle license? Anything above 50cc. Below is a simplified chart, but keep in mind that some states introduce additional restrictions on speed or classification of mopeds vs. scooters. Riders under 18 may also face special permit conditions.
| Engine Size | License Requirement |
| Under 50cc | Usually no license |
| 50cc to 125cc | Motorcycle permit/license needed; sometimes restrictions on highways |
| 125cc+ | Full motorcycle license class, often with age requirements |
Outside the chart, California, Florida, and Texas could vary a bit when it comes to their treatment of mopeds.
One such example is that 50cc mopeds on a standard driver’s license are allowed in certain but not all states, but 50cc mopeds on a motorcycle endorsement are allowed in all states. These differences should be observed by you as a business distributor when placing the products in the local markets.
The EU has stricter, tiered systems, structured to gradually introduce riders to more powerful motorcycles:
Other markets, such as Australia, Canada, and parts of Asia, follow hybrid systems. Australia, for example, uses LAMS (Learner Approved Motorcycle Scheme), where cc and power are both factored.
In Asia, smaller motorcycles (100 to 150cc) dominate the market, but most jurisdictions still require a licence even at those lower engine sizes.
There are several categories where the cc limit does not tell the full story. Here are the exceptions to keep in mind:
Yes. You can purchase a motorcycle without having a license. Dealerships generally do not require proof of license to sell you a bike. However, riding it legally is another story.
Insurance and registration in most states demand a valid motorcycle license class, so buyers cannot operate their new motorcycle on public roads until licensing requirements are met.
For a motorcycle to be considered street legal, it must be equipped with features like headlights, taillights, mirrors, turn indicators, a VIN, and registration plates. Off-road motorcycles, such as dirt bikes, typically lack these, meaning they cannot be used on public roads.
Some riders opt for street conversion kits, adding essential features like lights for dirt bikes and mirrors to make them compliant. For riders who want the convenience of urban commuting, small street legal motorcycles under 50cc, and increasingly, electric mopeds are a growing trend.
In the case of the motorcycle business, cc limits affect demand as well as compliance in the market. In high-population cities, 50cc and 125cc vehicles are the most common in the rental markets and mobility services because they are affordable and easy to maintain. They are also used in commercial fleets as they are easy to handle and are economical.
Apollino recognizes these needs. This is the reason why we provide street-legal motorcycles with varying licensing needs in different regions. Our models that are compliance-based make distributing less difficult, sales easier, and legal issues less risky. Having entry-level and advanced, export-ready solutions that are available worldwide, in entry and wholesale options, Apollino makes sure that the dealers will be able to cater to the needs of the customers.
Motorcycle licensing rules continue to evolve. Many countries are tightening regulations, requiring more extensive training and testing for higher classes. Electric bikes, which are often equivalent to sub-50cc models in performance, are gaining special regulatory attention.
Hybrid systems that consider both cc and kilowatt output are becoming more common, balancing safety with the shift toward alternative fuel motorcycles.
So, what is the highest cc without a motorcycle license? In most regions, the answer remains 50cc. Yet it’s crucial to note that exceptions apply, and riders must always verify local laws before getting on the road.
At Apollino, we supply street legal motorcycles for every motorcycle license class, making us the ideal partner for distributors, dealers, and rental operators. By choosing Apollo, you gain access to compliant, market-ready solutions with wholesale opportunities across all levels of motorcycles.
APOLLO stands at the forefront as a top-tier manufacturer specializing off-road motorcycles, with the aim to spread its network worldwide. Join hands with our fantastic team. You can get instant quotes and order deliveries with the best quality products.
Connect with us today to join the ride towards innovation and explore the thrilling world of off-road adventures!
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site. By using our site you consent to cookies.
Table of Contents
×